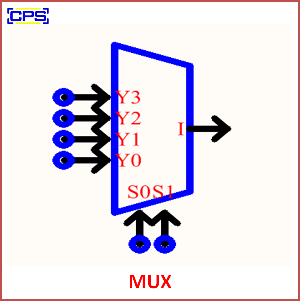
A MUX (short for Multiplexer) is a digital device that selects one input signal from multiple inputs and forwards it to a single output line. It operates based on the value of control signals, which determine which input to connect to the output.
Key Features of a Multiplexer:
- Many-to-One Selection:
- A MUX combines multiple input signals and selects one for output, acting as a data selector.
- Control Signals:
- The selection of a specific input is determined by control or selection lines, whose binary combination corresponds to the chosen input.
- Digital Logic:
- MUX devices are implemented using digital logic gates and are integral to combinational logic systems.
Types of Multiplexers:
- 2-to-1 MUX: Selects one of two inputs based on one control signal.
- 4-to-1 MUX: Selects one of four inputs using two control signals.
- 8-to-1 MUX, 16-to-1 MUX, etc.: Larger multiplexers allow selection from more inputs using more control lines.
Applications of a Multiplexer:
- Data Routing:
- Used in communication systems to transmit data from multiple sources over a single channel.
- Microprocessor Design:
- MUX devices are used to select data or instructions for processing.
- Signal Processing:
- Help in combining signals from different sensors or sources for further analysis.
- Logic Design:
- Used in the implementation of complex digital circuits and logic functions.
- Switching Systems:
- Enable efficient routing of signals in networks and telecommunication systems.
Advantages:
- Reduces the number of wires and connections needed in a circuit.
- Simplifies circuit design by enabling selection from multiple sources.
- Versatile in both digital and analog signal processing.
Disadvantages:
- Limited by the number of inputs it can handle, requiring cascaded designs for large systems.
- May introduce slight delays due to the internal logic switching.
In summary, a MUX (Multiplexer) is a vital component in digital electronics, enabling the selection of one signal from multiple sources for routing, processing, or transmission, making it indispensable in communication and computing systems.
