A NOR gate (short for NOT OR gate) is a fundamental digital logic gate that performs the inverse of the OR operation. It outputs a logical HIGH (1) only when all its inputs are LOW (0); otherwise, it outputs a logical LOW (0).
Key Features of a NOR Gate:
- Boolean Expression:
- The output (YYY) of a NOR gate is expressed as: Y=A+B‾Y = \overline{A + B}Y=A+B where AAA and BBB are the inputs.
- It is the negation ( ‾\overline{\ } ) of the OR operation.
- Truth Table:
| Input A | Input B | Output Y (A+B‾\overline{A + B}A+B) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
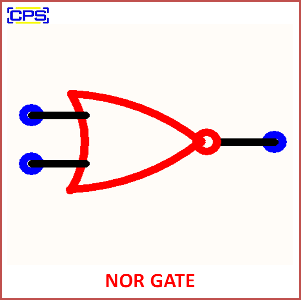
- Symbol:
- A NOR gate is represented by an OR gate symbol with a small circle (representing negation) at its output.
Applications:
- Universal Gate:
- A NOR gate is called a universal gate because it can be used to construct any other logic gate (AND, OR, NOT, NAND, XOR) and perform complex logical operations.
- Digital Logic Design:
- Used in the design of digital circuits and systems.
- Control Systems:
- Commonly employed in control circuits for decision-making processes.
- Memory Circuits:
- Found in storage elements like flip-flops and latches.
Advantages:
- Simplifies circuit design since it can implement other logic gates.
- Useful in minimizing the number of components in certain designs.
Disadvantages:
- May introduce propagation delay in large or complex circuits due to cascading gates.
In summary, a NOR gate is a versatile digital logic gate that combines the properties of OR and NOT operations, making it an essential component in digital electronics for constructing and optimizing logical circuits.
