A Step-Down Transformer is an electrical device that reduces the voltage level from its input (primary winding) to its output (secondary winding) while maintaining the same power level, apart from minor losses. It works based on the principle of electromagnetic induction and is commonly used to supply lower voltage levels to electrical equipment.
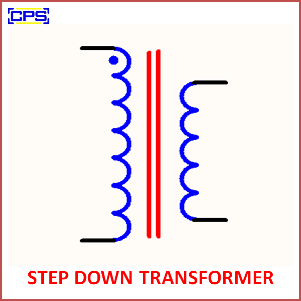
Key Features of a Step-Down Transformer
- Voltage Reduction:
- Converts high voltage at the primary side to a lower voltage at the secondary side.
- Winding Configuration:
- The primary winding has more turns of wire than the secondary winding, creating the step-down effect.
- Magnetic Core:
- Made of laminated iron or other magnetic materials to facilitate efficient energy transfer.
Working Principle:
- Electromagnetic Induction:
- When an alternating current flows through the primary winding, it creates a magnetic field in the core, inducing a voltage in the secondary winding. The reduced number of turns in the secondary winding results in a lower output voltage.
Applications of Step-Down Transformers:
- Power Distribution:
- Reduce high transmission voltages to safe levels for residential or commercial use.
- Electronic Devices:
- Power adapters for low-voltage devices like laptops and chargers.
- Industrial Equipment:
- Powering machinery requiring lower voltages.
- Testing and Measurement:
- Providing adjustable voltage levels in laboratories.
Advantages:
- Efficient energy transfer with minimal losses.
- Provides electrical isolation between input and output.
- Durable and reliable for long-term operation.
Disadvantages:
- Only suitable for AC circuits.
- Inefficient at very low loads.
- Initial installation cost can be high for large transformers.
