A controlled voltage source is an active circuit element that provides an output voltage that is proportional to a controlling input signal. The voltage source maintains a specified voltage across its terminals, independent of the current drawn, within its operational limits.
Key Features of a Controlled Voltage Source:
- Input Control:
- The output voltage is governed by an input signal, which can be:
- A voltage (Voltage-Controlled Voltage Source, VCVS).
- A current (Current-Controlled Voltage Source, CCVS).
- The output voltage is governed by an input signal, which can be:
- Output Voltage:
- Delivers a voltage that varies or remains constant depending on the control input.
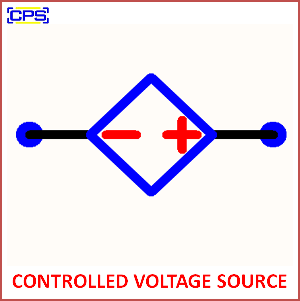
- Symbol:
- Represented in circuit diagrams with a diamond shape enclosing a “+” and “-” sign, indicating controlled voltage.
Types of Controlled Voltage Sources:
- Voltage-Controlled Voltage Source (VCVS):
- The output voltage is proportional to an input voltage signal.
- Current-Controlled Voltage Source (CCVS):
- The output voltage is proportional to an input current signal.
Applications:
- Signal amplification in analog circuits.
- Simulation of voltage sources in circuit analysis and modeling.
- Feedback control systems in electronics.
- Power supplies with adjustable voltage output.
Controlled voltage sources are critical in electronic circuit design, enabling precise control of voltage in response to external signals.
