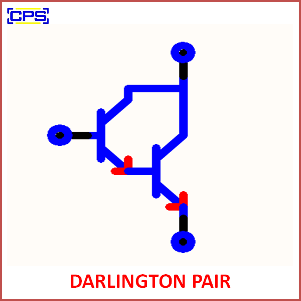
A Darlington pair is a configuration of two bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) connected together to amplify current. It functions as a single transistor with a much higher current gain, making it useful in applications where a high current amplification factor is required.
Key Features of a Darlington Pair:
- Structure:
- The emitter of the first transistor is connected to the base of the second transistor.
- The two transistors share a common collector terminal.
- High Current Gain:
- The overall current gain (βtotal\beta_{total}βtotal) is the product of the gains of the two transistors: βtotal=β1⋅β2\beta_{total} = \beta_1 \cdot \beta_2βtotal=β1⋅β2
- Even small base currents can result in large collector currents.
- Voltage Drop:
- The base-emitter voltage drop is approximately twice that of a single transistor (about 1.2V instead of 0.6V).
Applications:
- Current Amplification: In circuits requiring high current gain, such as motor drivers and relay control.
- Power Applications: Used in audio amplifiers and power supplies.
- Switching Circuits: Serves as a switch in digital and control systems.
Advantages:
- High current gain.
- Simplifies circuit design by reducing the need for additional amplification stages.
Disadvantages:
- Increased base-emitter voltage drop.
- Slower switching speeds compared to a single transistor.
A Darlington pair is a simple and effective configuration for achieving high current amplification in electronic circuits.
