An NMOS transistor (N-channel Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor) is a type of MOSFET that uses an N-type semiconductor channel to control the flow of current. It operates by applying a voltage to the gate terminal, which allows or blocks current flow between the source and drain terminals.
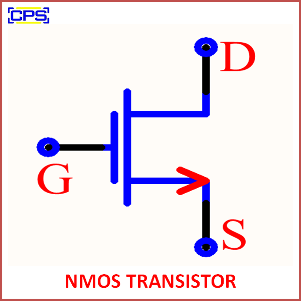
Key Features of an NMOS Transistor:
- N-Type Channel:
- The channel is made of an N-type semiconductor, where electrons are the primary charge carriers.
- Three-Terminal Device:
- Consists of three main terminals:
- Gate (G): Controls the flow of current.
- Source (S): The terminal where current enters.
- Drain (D): The terminal where current exits.
- Consists of three main terminals:
- Gate Control:
- When a positive voltage is applied to the gate (relative to the source), an electric field is created that attracts electrons, forming a conductive channel between the source and drain, allowing current to flow.
Operating Modes:
- Cutoff Mode:
- No channel is formed when the gate-to-source voltage (VGSV_{GS}VGS) is less than the threshold voltage (VthV_{th}Vth), and no current flows.
- Triode Mode:
- When VGSV_{GS}VGS exceeds VthV_{th}Vth and VDSV_{DS}VDS (drain-to-source voltage) is small, the transistor behaves like a resistor.
- Saturation Mode:
- When VGSV_{GS}VGS exceeds VthV_{th}Vth and VDSV_{DS}VDS is large, the current flow becomes independent of VDSV_{DS}VDS and depends on VGSV_{GS}VGS.
Applications:
- Digital Logic Circuits:
- Used in CMOS (Complementary MOS) technology along with PMOS transistors to implement logic gates and digital circuits.
- Amplifiers:
- Acts as a signal amplifier in analog circuits.
- Switching Applications:
- Commonly used as a switch in power electronics and digital systems.
- Integrated Circuits (ICs):
- Widely used in ICs for processors, memory, and other components.
Advantages:
- Faster switching speeds compared to PMOS transistors due to higher mobility of electrons.
- Efficient in handling large currents.
- Compatible with modern semiconductor manufacturing processes.
Disadvantages:
- Requires a positive gate voltage, which may necessitate additional circuitry in some designs.
- Susceptible to static discharge damage during handling.
In summary, an NMOS transistor is a critical component in modern electronics, offering high-speed operation and efficiency in applications ranging from logic gates to power control systems.
